- Sitemaps in SureRank
- How to Enable Video Sitemap in SureRank Pro
- How to Enable the News Sitemap in SureRank
- How to Show the HTML Sitemap on Your Site in SureRank Pro
- How to Regenerate the Sitemap After Excluding a Post Type in SureRank
- Change the Sitemap URL in SureRank
- How to Enable Author Sitemap in SureRank
- How to Fix WWW and Non-WWW Version Redirects to Improve Your SEO
- How to Fix: No H1 Heading Found on Your Homepage
- How to Fix Missing H2 Headings on Your Homepage
- Re-run Checks Button in SureRank
- Fix Critical Error: Another SEO Plugin Detected in SureRank
- Fix Warning: Site Tagline Is Not Set in SureRank
- How to Fix Multiple SEO Plugins Detected on Your Site
- How to Fix: Homepage is Not Indexable by Search Engines
- Warning: Homepage Does Not Contain Internal Links
- How to Fix Missing Alt Text on Homepage Images
- How to Fix Missing Canonical Tag on Your Homepage
- How to Fix Missing Open Graph Tags on Your Homepage
- How to Fix Missing Structured Data (Schema) on Your Homepage
- How to Fix XML Sitemap is Not Accessible in SureRank
- How to Fix Search Engine Visibility Blocked in WordPress
- Connect Google Search Console
- How to Fix Site Not Served Over HTTPS in SureRank
- How to Fix Robots.txt File Accessibility Issues in SureRank
- How to Fix Missing Search Engine Title on Your Home Page
- How to Fix Home Page is Not Loading Correctly
- How to Fix No Images Found on the Homepage Warning
- SureRank – Internal Link Suggestions
- How to Fix: Search Engine Title is Missing on the Page
- Page Level SEO: Broken Links Detected
- How to Fix Missing Alt Text on Images
- How to Fix Page URLs That Are Too Long
- Page Level SEO Warning: No Links Found on This Page
- Page Level SEO Warning: No Images or Videos Found
- Page Level SEO Warning: Missing Search Engine Description
- Page Level SEO Warning: No Subheadings Found on This Page
- Page Level SEO Warning: Canonical Tag is Missing
- Page Level SEO Warning: Open Graph Tags Missing
- What is Google Search Console and how does SureRank use it?
- Recommended Image Sizes
- SureRank – SEO Check Severity Guide
- Using SureRank with Other SEO Plugins – Best Practices
- Import/Export Feature – SureRank Plugin
- What is llms.txt and Does SureRank Support It?
- Does SureRank offer a keyword rank-tracking feature?
- Does SureRank Come With Google Analytics Integration?
- Customize Final Title Tag surerank_final_title
- Customize Post Type Archive Title Output surerank_post_type_archive_title
- Customize Archive Page Title with surerank_archive_title
- CustomizeModify the Search Results Page Title surerank_search_title
- Customizing the 404 Page Title surerank_not_found_title
- Customizing the Title Separator surerank_title_separator
- How to Remove Archive Prefixes from Titles Using SureRank
- Customize Homepage Pagination Format surerank_homepage_pagination_format
- Customize Maximum SEO Title Length surerank_title_length
- Enable/Disable Pagination in SureRank Archives surerank_show_pagination
How to Fix WWW and Non-WWW Version Redirects to Improve Your SEO
If you’ve received a critical SEO warning in SureRank saying:
“Site does not correctly redirect between www and non-www versions”
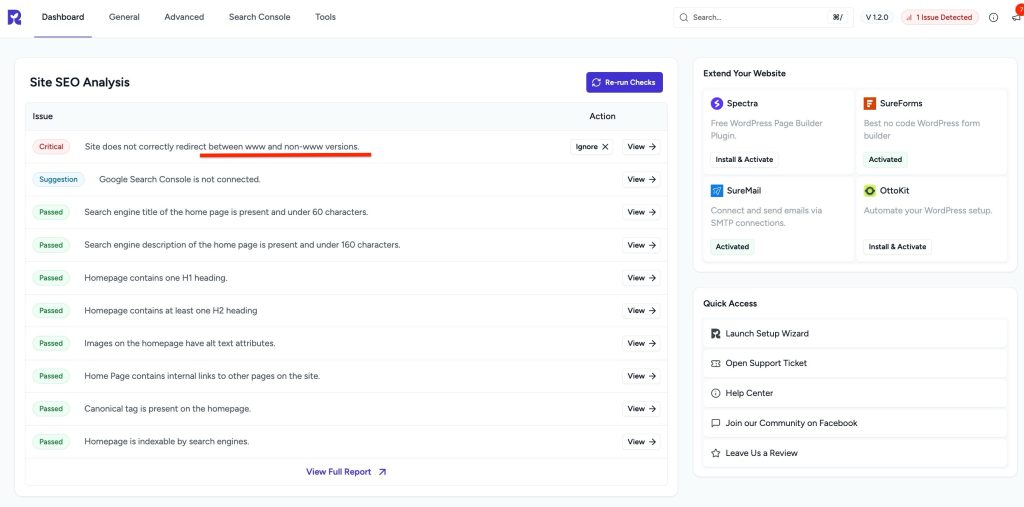
This article will help you understand what this means, why it’s important, and how to fix it even if you’re not a technical person.
What’s the Problem?
Your website can often be accessed using two different versions:
Both might show the same content. But unless one version automatically redirects to the other, search engines treat them as two different websites.
That means your site is being split into two copies, and each page exists in two places even though it’s the same content.
Why This Matters for SEO
Search engines like Google see example.com/page and www.example.com/page as two separate URLs.
That leads to:
- Duplicate Content: Google might think you have copied content on your own site.
- Split Link Equity: Backlinks could be divided across both versions, reducing your domain authority.
- Confused Search Engines: Google may not know which version to index or show in search results.
- Wasted Crawl Budget: Googlebot may crawl both versions unnecessarily, wasting its time.
In short: This hurts your SEO performance.
Who Should Fix This?
If you’re not technical or don’t feel confident editing server files:
We strongly recommend you contact your hosting provider’s support team and ask them to help you redirect one version of your site to the other.
Here’s what you can say:
Hi,
I want to set up a 301 redirect so that my website always loads either the www or non-www version (only one).
Can you help me configure that redirect on the server?
But if you are comfortable making edits yourself, or your host doesn’t offer help, read on.
Step 1: Choose Your Preferred Version
There is no SEO difference between using www and not using it. It’s just a personal preference.
- Want your site to show as https://www.example.com? Then redirect everything from example.com to www.example.com
- Prefer it cleaner as https://example.com? Then redirect everything from www.example.com to example.com
Just pick one and stick with it.
Step 2: Redirect Using .htaccess (for WordPress on Apache Servers)
If your site is hosted on Apache (most shared hosting like Bluehost, HostGator, SiteGround), follow these steps.
How to Edit the .htaccess File
- Go to your hosting control panel (like cPanel)
- Open the File Manager
- Find the .htaccess file in the public_html folder
- Right-click → Edit
If you don’t see the .htaccess file, make sure hidden files are visible.
A) Redirect www → non-www
If you want your website to always load without www:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www\.(.+)$ [NC]
RewriteRule ^ https://%1%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]Explanation:
- RewriteEngine On: Enables URL rewriting
- RewriteCond: Checks if the URL starts with “www.”
- %1: Captures everything after www.
- R=301: Permanent redirect (best for SEO)
- L: Last rule, stop processing further
B) Redirect non-www → www
If you want your website to always load with www:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^www\. [NC]
RewriteRule ^ https://www.%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]Explanation:
- This checks if the URL does not start with www and redirects it to include www
- %{HTTP_HOST} pulls the current domain (e.g., example.com)
- %{REQUEST_URI} pulls the rest of the path (e.g., /about)
Important Tips
- Always keep a backup of your original .htaccess file before editing.
- Make sure you already have SSL (https://) working. These redirects assume your site is secure.
- If you already have other rewrite rules (like for WordPress), add this above the # BEGIN WordPress section.
Step 3: Test the Redirect
Once you’ve added and saved the changes:
- Try visiting the non-preferred version in your browser.
- e.g., go to https://www.example.com
- It should automatically redirect to your preferred version — e.g., https://example.com
- Use tools like:
- https://httpstatus.io
- https://redirect-checker.org
- Or just open Developer Tools (F12) → Network tab → Check redirect status (301)
If it doesn’t work, double-check your .htaccess for typos or contact your hosting provider.
Step 4 (Optional): Set Preferred Domain in Google Search Console
If you use Google Search Console, make sure to:
- Add both versions of your site:
- https://example.com
- https://www.example.com
- In the property settings, choose your preferred version
This helps Google understand your site’s structure better.
What About NGINX Servers?
If your server uses NGINX (common in VPS or cloud setups), the redirect must be configured in your server block.
Here’s an example for NGINX (not for beginners):
A) Redirect www → non-www:
server {
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}B) Redirect non-www → www:
server {
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://www.example.com$request_uri;
}You’ll need to restart NGINX after making changes. If unsure, ask your hosting company to do it.
Summary
- SEO depends on having one canonical domain, not both www and non-www
- Choose one version
- Use .htaccess (for Apache) or NGINX config to redirect the other version
- Use 301 redirects, not JavaScript or meta refresh
- Test thoroughly
Need Help?
If you’re unsure or get stuck: Reach out to your hosting provider and ask for help setting up a redirect between www and non-www.
Getting this right improves your site’s SEO and prevents future indexing issues.
We don't respond to the article feedback, we use it to improve our support content.